
Mastering the Divisional Organization Chart: Structuring for Specialization
As a company grows and diversifies its operations, managing multiple products, services, or regions within a unified structure can become complicated. That’s where the divisional organization comes in. Designed to provide autonomy and focus on specific areas of business, the divisional structure is ideal for large companies with diverse offerings or extensive operations.
What is a Divisional Organization Chart?
The divisional organization design is a structural model in which a company is divided into semi-autonomous units, called divisions, based on product lines, geographic locations, markets, or services. Each division operates like a small company, with its own functional teams, such as sales, marketing, HR, and operations. Each division typically reports to headquarters or senior management, but has the freedom to make decisions within its own area of expertise. The divisional organization design differs itself from standard hierarchical organizational structure, As hierarchical organizational structure is characterized by a clear chain of command, where authority and responsibility flow vertically from top management to lower levels. In contrast, a divisional organizational structure divides the company into separate, semi-autonomous units or divisions, often based on product, market, or geographic area.
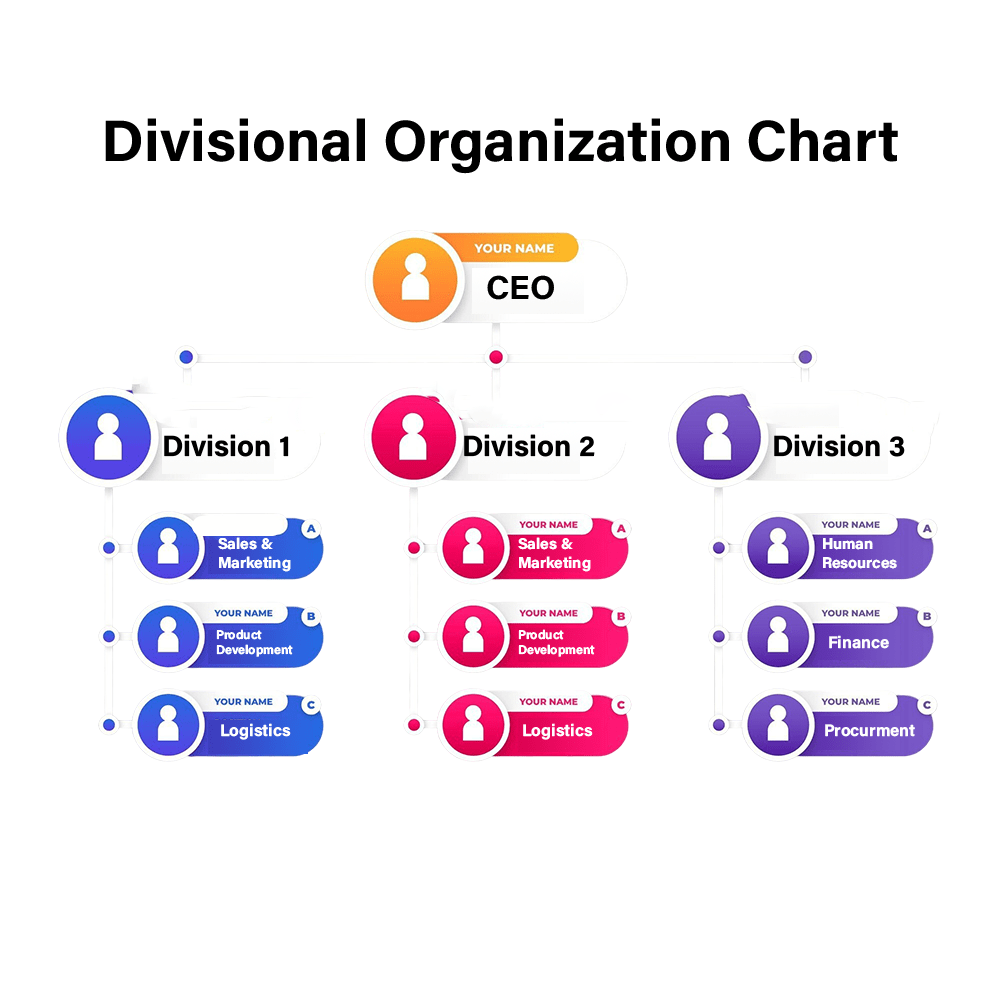
Key Features of a Divisional Organization Chart
- Division-Based Structure: The company is split based on product, service, geography, or customer type.
- Independent Functional Units: Each division has its own departments like sales, HR, and finance.
- Performance Accountability: Each division is often treated as a profit center, with performance measured independently.
- Corporate Oversight: While divisions have autonomy, strategic direction and governance come from the top leadership.
Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing a Divisional Organization Chart
1: Identify Division Criteria
Decide how you want to split the organization by product, service, region, customer.
2: Define Division Heads and Leadership Roles
Appoint division managers or directors who will lead each unit and report to senior management.
3: Map Out the Reporting Structure
Show how employees report to their functional heads and how those heads report to division managers.
4: Align with Company Strategy
Ensure the divisional setup aligns with your broader business goals and market approach.
5: Communicate the Structure
Roll out the new chart company-wide, clarifying roles and expectations for each division.
Benefits of a Divisional Organization Chart
Focused Strategy Execution by tailor its operations to its market, product, or region.
Improved Accountability with tracking performance and profitability by division.
Greater Flexibility make quick decisions without waiting for corporate approval.
Customer-Centric Approach with the specific needs of a product group or region.
Leadership Development as Divisional heads gain experience that prepares them for executive leadership roles.
Best Practices for Implementing a Divisional Organization Chart
1. Divisional organization chart set boundaries for what decisions division leaders can make independently.
2. Standardize Reporting as divisions are autonomous, consistent KPIs and reporting tools are essential for unified oversight.
3. Provide freedom but monitor performance closely with regular reviews.
Conclusion
A divisional org chart works well for companies that manage multiple product lines or operate in multiple markets. It promotes agility, specialization, and a greater focus on results at all levels. While it requires strong leadership and careful coordination, the benefits of scalability and responsiveness are worth the effort. By thoughtfully and strategically implementing a divisional structure, you can turn complexity into a competitive advantage and enable your company to grow in every industry, market, and region in which it operates.