-min.png)
Simplifying Flat Organization Chart: A Modern Approach to Structure
With modern times many companies are moving away from traditional hierarchies and adopting flatter structures. Among them, the flat org chart stands out as a popular model that promotes collaboration, speed, and flexibility. Whether you’re running a startup or modernizing an existing organization, understanding how a flat structure works is essential to driving innovation and efficiency.
What is a Flat Organization Chart?
A horizontal organizational chart is a visual representation of a company's structure, with minimal or no middle management layers between employees and management. Unlike hierarchical models that have many levels of authority, a flat organization promotes equal levels of responsibility and direct communication between employees and senior management.
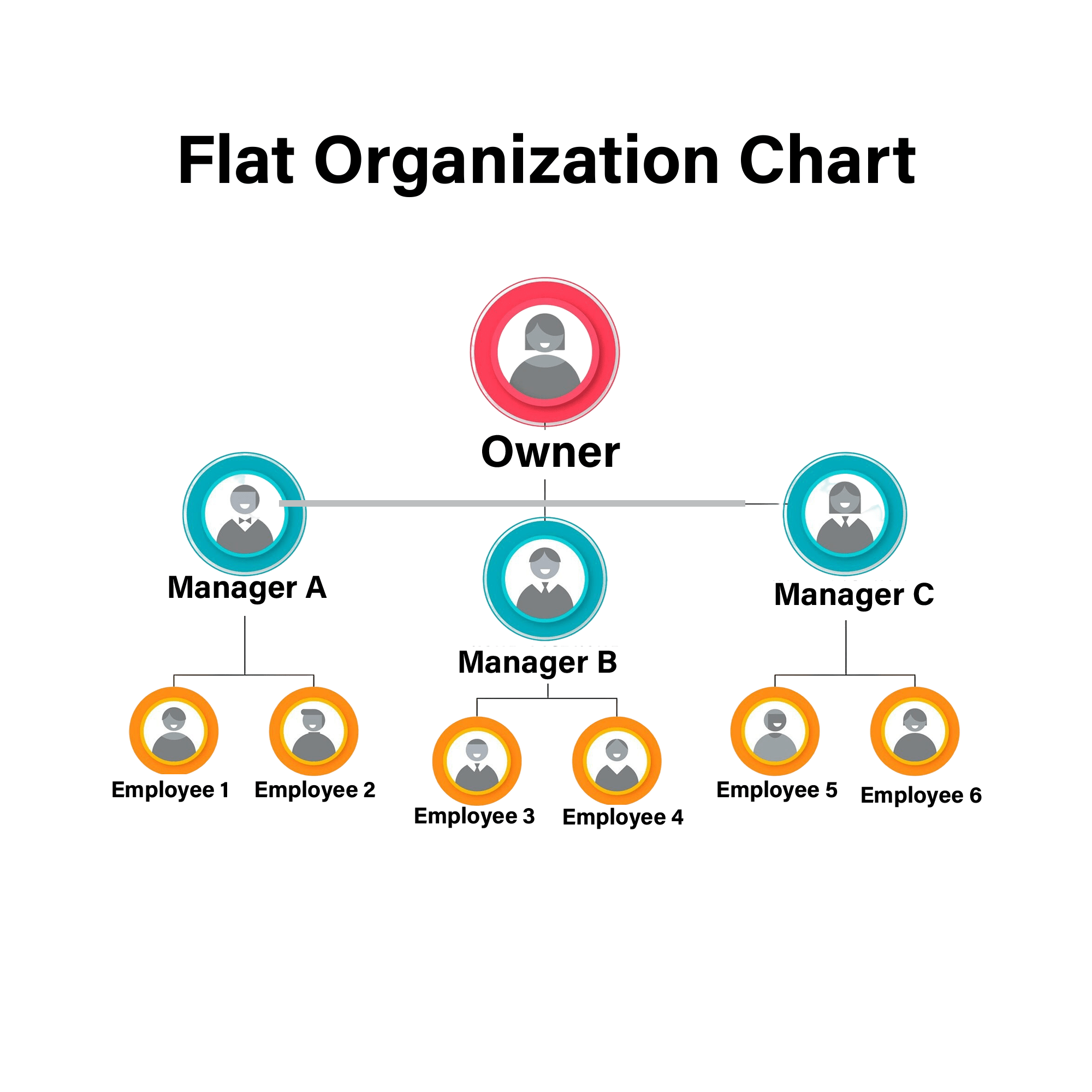
Key Features of a Flat Organization Chart
- Fewer Management Levels: There are typically one or two layers of management, or sometimes none at all between the workforce and leaders.
- Wider Spans of Control: Managers supervise more employees directly, reducing the need for multiple supervisory roles.
- Decentralized Decision-Making: Decision-making is more democratic and often involves team input rather than top-down commands.
- Open Communication: Unlike rigid hierarchies, workflows in a matrix structure can adapt to changing business priorities.
Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing a Flat Organization Chart
1: Evaluate Organizational Readiness
Make sure your company culture promotes open communication, self-control, and a collaborative work style.
2: Identify Core Teams and Roles
Define key teams or departments and assign them clear roles without adding unnecessary layers of management.
3: Establish Direct Communication Channels
Introduce tools (e.g. Slack, MS Teams, etc.) and habits that enable direct contact between employees and management.
4: Create the Chart
You can use tools like Lucid chart, Google Drawings, or OrgChart.js to visualize the structure. Put senior management at the top (or in the middle) and provide direct links to all teams or functions.
5: Define Responsibilities Clearly
Even without titles, responsibilities should be documented to avoid role confusion and overlaps.
6: Encourage a Culture of Accountability
With fewer managers, individuals must take responsibility for their tasks and results.
Benefits of a Flat Organization Chart
Faster Communication with Fewer layers means quicker decisions and problem-solving.
Greater Involvement employees feel more valued and engaged when their voices are heard.
Reduced Operational Costs by eliminating excess management reduces payroll and overhead.
Employees gain exposure to multiple functions, enhancing their skills and career development.
Agility and Flexibility to adapt to change and pivot strategies.
Best Practices for Implementing a Flat Organization Chart
1. Build a culture where employees feel safe to voice ideas, concerns, and feedback.
2. Promote team-based work rather than siloed individual contributions.
3. As your organization grows, you may need to reintroduce light structure without abandoning the flat model.
4. Reassess how the flat model is working and make improvements as needed.
Conclusion
The flat org chart is more than just a structure—it’s a mindset. It promotes agility, innovation, and integration, making it ideal for startups, creative teams, and modern organizations. While a flat org chart isn’t a perfect fit for every company, when implemented carefully, it can unlock the incredible potential of your employees.